Numerical Modeling
The ANSYS Fluent program offers two different approaches to multiphase modelling:
1) Euler-Lagrange approach: In this approach, the primary phase is in a continuum by solving the Navier-Stokes equations, while the secondary phase is solved as a large number of particles, bubbles or droplets as the phase dispersed throughout the calculated flow area. During the calculation of the primary phase, the trajectories of the secondary phase are calculated separately at the specified intervals. The primary and secondary phase provide the exchange of mass, momentum and energy between them.
2) Euler-Euler approach: In this approach, different phases are handled mathematically and the volume percentages of the phases are defined in the range of zero to one. The volumetric ratios of the different phases are continuous functions of time and space, and their sum is assumed to be one. In the model, “VOF Model”, “Mixture Model” and the most comprehensive “Euler Model” options are available for the Euler-Euler approach. According to the experimental results, the most suitable model will be selected for the numerical modeling of the polyphase flow.
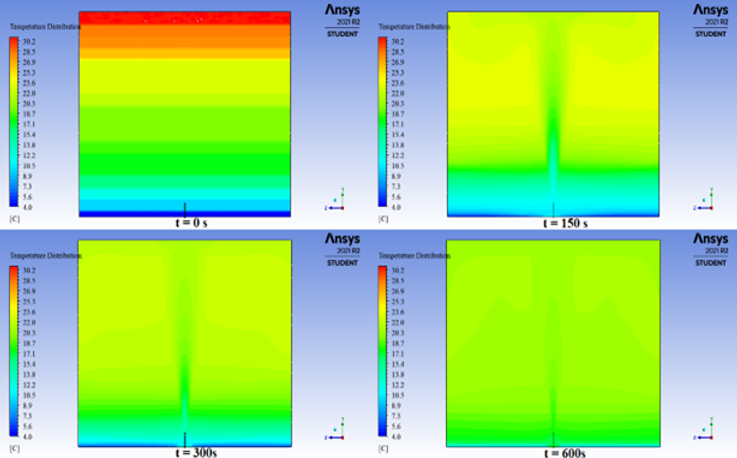
Numerical simulation of the preliminary experiments was done with the Euler model. In the experimental setup, when 400 l/h of air is supplied to the initially stratified stream from a 2 mm diameter single-hole diffuser, the hydrodynamics of the observed mixture is modeled by choosing the current boundary condition ‘degassing’ (Fig.5.)
Modeling the mixture of thermally stratified water column with air bubble requires turbulent modeling of two-phase flow. The 3D Fluent model, which is widely used in turbulent flow, can model with four different methods. Literature studies conducted within the scope of preliminary simulations pointed out that the “discrete phase method” and “volume of fraction method” methods are not suitable for the study. For this reason, the methods used in the numerical model are limited to the “Mixture” and “Eulerian multiphase” models. In the simulations using the two models separately, it has been observed that the “Eulerian multiphase” model can model the experimental results when “degassing” is used as the boundary condition (Elçi et al., 2023).

c d
Fig.6. a. Savonius Wind Turbine Cross Section Wind Speed Animation b. Savonius Wind Turbine Bird’s Eye Wind Speed Animation
e f
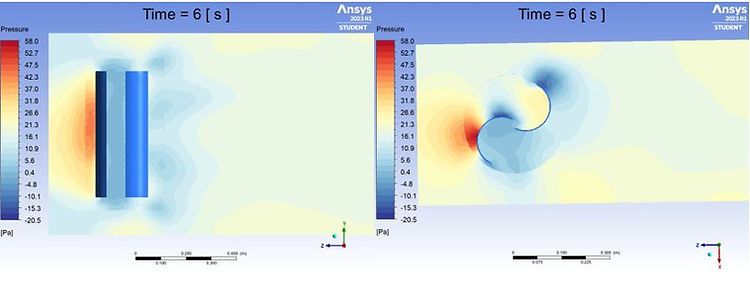
Fig.7. to. Savonius Wind Turbine Side Section Wind Pressure Animation f. Savonius Wind Turbine Bird’s Eye Wind Pressure Animation
