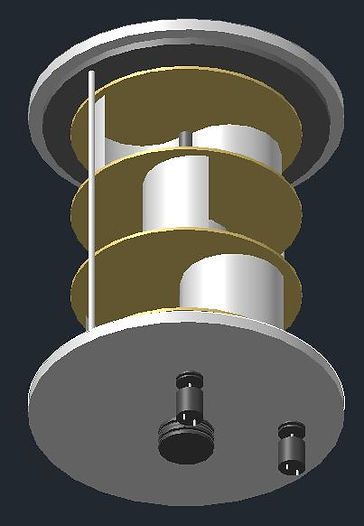
The Aim Of The Project
The main purpose of our project is to control the growth of cyanobacteria in dam reservoirs. For this purpose, it is aimed to design an autonomous system with the use of an artificial mixture whose energy is provided from renewable energy sources. Thus, it will be possible to effectively prevent and control the growth of cyanobacteria in the dam chambers. Since this system is designed to monitor the water quality continuously and naturally and intervene when necessary, it is aimed to keep the water quality in the dam reservoirs under regular control.
The targets set to achieve this aim are as follows;
Both the air diffuser and the water pump will be used to optimize the water mixture and the efficiency of both systems will be evaluated based on the test results separately.
The efficiency of the water pump and air diffuser systems will be modeled by determining their peak design using the ANSYS FLUENT numerical model.
- In order for the mixture to start autonomously (spontaneously), an ardunio-controlled system will be designed that measures the temperature/dissolved oxygen values and starts the mixture when a certain threshold value is passed.
Cyanobacteria will be inoculated into the test tank at concentrations determined by measuring the temperature/dissolved oxygen values. After this stage, temperature changes in the water column will be monitored to determine the mixing efficiency. The efficiency of the selected mix designs in removing the existing cyanobacteria will be investigated.
Based on the experimental and numerical results, an optimum design proposal will be presented for cyanobacteria control and increasing the oxygen level in the water column of the dam reservoirs.
Based on the results of the study, the optimal artificial mixing system for Tahtalı dam reservoir water intake structure will be proposed by scaling with Weber analysis method. The performance of this proposed system will be examined using numerical modeling technique.
The ultimate goal of our project is to design an optimized artificial mixing system for the reduction of cyanobacterial biomass in dam reservoirs, powered by wind energy, managed by dissolved oxygen and temperature parameters. To achieve this goal, an optimum design for the wind turbine for the energy of the artificial mixture will be proposed and then the performance of the prototype will be examined using the numerical modeling method.
WHAT IS CYANOBACTERIA?
Cyanobacteria is one of the photosynthetic microorganisms in the water columns. It synthesizes organic molecules using sunlight and gases (especially carbon dioxide) and disrupts the natural balance of water columns. The overgrowth of cyanobacteria deteriorates the water quality and makes it necessary for water treatment in dam reservoirs.
In the reservoirs, invasions of cyanobacteria and blue-green algae often occur due to tropical temperatures combined with nutrient flow from the basins.
Worldwide warming and temperature changes can drastically alter species compositions and cause the growth of toxic phytoplankton.
The ability of cyanobacteria to produce toxins can have harmful consequences for human health.

CYANOBACTERIA DAMAGES AND DAMAGES TO WATER STRUCTURES
Deterioration of Water Pumping Systems
Cyanobacteria can clog and damage water pumping systems' pipes and machine parts.
Water Density
Changes
Large production of cyanobacteria can cause changes in water density, which can damage the structure of dams and water structures.
Pollution
Cyanobacteria can produce large amounts of phytoplankton and pollute water supplies
Ecological Impacts
Cyanobacteria can kill other aquatic life and destabilize aquatic ecosystems
Toxic Effects
Cyanobacteria can produce toxic substances, which can degrade the quality of water supplies and affect animals and humans.
WHAT IS RENEWABLE ENERGY?
Renewable energy sources are energy sources obtained from natural sources that are unlimited or self-renewable. Unlike fossil fuels, these resources are constantly renewable and have less negative impact on the environment. Renewable energy sources include solar, wind, hydraulic, biomass and geothermal energy sources.
Wind energy is obtained by converting the wind’s kinetic energy into electrical energy through wind turbines. These turbines convert the movement energy of the wind into mechanical energy with their rotating blades and electrical energy is produced through generators. Wind energy is a renewable and clean energy source without consuming natural resources or generating waste.
Wind energy occupies an important place among renewable energy sources. Wind power plants have been established in many countries around the world and these power plants produce high amounts of electricity. Wind energy helps to minimize negative impacts on the environment by reducing the use of fossil fuels. In addition, wind energy sources are becoming increasingly popular, especially due to their low energy costs

SAVONIUS WIND TURBINE
Turbines are generally categorized as vertical axis or horizontal axis. Savonius wind turbines are in the vertical axis turbine category. They simply consist of two half-cylindrical turbine blades positioned between two horizontal plates and their centers separated along the axis. It was first invented by Finnish engineer Sigurd Savonius in 1922 and patented in 1926.
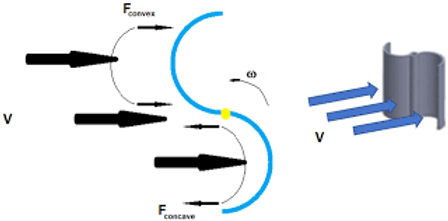
The incoming wind in Savonius turbines, whose working principles are quite simple, creates positive moment in the concave blades and negative moment in the convex blades of the turbine. The turbine starts radial movement since the moment generated in the concave blades is greater than that of the convex blade due to aerodynamic effects.
- It is possible to list the advantages of Savonius turbines as follows.
- Suitable for applications requiring high torque.
- It can start working even at low wind speeds.
- They are easy to manufacture and design.
- Since they meet the wind from all directions, they do not need a rudder system to turn the turbine to the wind direction.
- Maintenance costs are low.
However, since they are highly exposed to wind resistance and friction, their efficiency is low and they are generally not preferred for generating energy. They are generally used to pump water in rural areas or applications requiring similar high torque values.